13 Things That Can Affect Fertility
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), infertility affects approximately 17.5% of the adult population worldwide. This means about one out of every six individuals experience some degree of infertility. While in the past, infertility focused primarily on female factors; it’s been found to affect both sexes fairly equally. Infertility can also be temporary or permanent, but there are several factors that come into play. To help you better understand your circumstances, we’ll go over 13 things that can affect fertility and what to do if you’re having trouble conceiving.
Symptoms of Infertility
Infertility is the inability to conceive a child after 12 months of unprotected sex. However, there may be other things that could indicate fertility problems. Some of the common signs or symptoms of infertility in women include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Absence of menstrual periods
- Painful or heavy menstrual periods
- Pain during intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Hormonal imbalances
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Endometriosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Multiple miscarriages
Common symptoms of infertility in men include:
- Low sperm count
- Abnormal sperm morphology
- Erectile dysfunction
- Difficulty maintaining an erection
- Pain, swelling, or lump in the testicle area
- Hormonal imbalances
- Varicocele
- Retrograde ejaculation
- Blockages in the ejaculatory ducts
If you’re having difficulty conceiving or are experiencing any of the symptoms above, it’s best to see your doctor for fertility screenings.
13 Things That Can Affect Fertility
That said, some things can affect fertility before you show any signs. By educating yourself on these factors, you can make healthier choices that support your reproductive health or get help from your doctor before you start trying to conceive.
1. Age
Age is a significant factor that impacts fertility, primarily in women. This is because women are born with a finite number of eggs, and as they get older, the quantity and quality of their eggs decline. As a result, women in their late 30s and 40s may face challenges conceiving naturally, and the risk of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome increases.
In contrast, men generally experience a more gradual decline in fertility with age. While men can continue to produce sperm throughout their lives, the quality of sperm may deteriorate over time, leading to reduced fertility. Advanced paternal age has also been associated with a slightly higher risk of certain genetic conditions and a longer time to conceive.
2. Hormones
Hormones also play a vital role in fertility. In women, hormones such as estrogen and progesterone regulate the menstrual cycle, preparing the uterus for pregnancy and ensuring the release of eggs from the ovaries. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are also necessary for ovarian function. FSH stimulates the growth of follicles that contain eggs, while LH triggers ovulation, releasing the mature egg for potential fertilization. Imbalances in these hormones can disrupt ovulation and lead to fertility issues. Hormones also influence the uterine environment in women, which is essential for implantation and early pregnancy development.
In men, luteinizing hormones (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) regulate the production of sperm in the testes. LH stimulates the production of testosterone, which is necessary for sperm production, while FSH supports the development of sperm cells. Hormonal imbalances can affect the quantity and quality of sperm, impacting male fertility.
3. Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for optimal fertility, as overweight and underweight individuals may experience difficulties conceiving. Extra body weight can disrupt hormonal balances in women, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and ovulation problems. Obesity is also associated with an increased risk of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can cause hormonal imbalances and hinder fertility. Over time, excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, further disrupting reproductive hormones. Being underweight can also be harmful to healthy hormonal balance.
In men, obesity has been linked to lower sperm quality and reduced fertility. While extra body weight also impacts hormonal levels, which can lead to low testosterone, higher oxidative stress, and inflammation—all of which affect sperm health. Being underweight can also reduce sperm production and negatively impact sperm motility.
4. Smoking
Smoking has a detrimental impact on fertility for both men and women. It can disrupt hormonal balances, interfere with the development and release of eggs, and increase the risk of reproductive disorders such as endometriosis. It also damages the DNA in eggs, leading to an increased risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy. Smoking may also accelerate the loss of eggs in women, resulting in an earlier onset of menopause.
In men, smoking is associated with decreased sperm count, reduced sperm motility, and increased abnormalities in sperm shape and function. Therefore, quitting smoking is crucial for improving everyone's fertility outcomes and overall reproductive health.
5. Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the hormonal balance, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and ovulation problems in women. Alcohol can also affect the development and quality of eggs, potentially reducing the chances of successful fertilization and implantation.
In men, alcohol use can impair sperm production and function, leading to reduced sperm count, motility, and morphology. It can also disrupt hormone levels and contribute to erectile dysfunction.
6. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Certain STIs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women. This can lead to scarring and damage to the reproductive organs, including the fallopian tubes and uterus, which may prevent eggs from reaching the uterus. This increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy, which is dangerous for both mom and baby.
In men, STIs can cause inflammation and damage the reproductive system, decreasing sperm quality and motility. STIs like syphilis and human papillomavirus (HPV) can also have long-term effects on fertility for both men and women and increase the risk of complications during pregnancy.
7. Medications
Some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy used in cancer treatment, can damage reproductive organs, including the ovaries and testes, leading to temporary or permanent infertility. Other medications, such as certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antiepileptic drugs, may affect hormone levels and disrupt the normal functioning of the reproductive system. Medications used to treat chronic conditions like hypertension or autoimmune disorders may also have side effects that can interfere with fertility.
8. Stress
Stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can interfere with the production and regulation of reproductive hormones. This disruption can affect the menstrual cycle in women and reduce sperm production or impair sperm quality. Try incorporating some deep relaxation techniques if you experience high levels of stress.
9. Sleep
Sleep deprivation can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting the release of reproductive hormones such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). In addition, sleep disturbances have also been linked to increased levels of stress hormones, which can further disrupt fertility.
10. Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental toxins such as pesticides, heavy metals, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can affect reproductive health in both men and women. These substances can interfere with hormonal balance, disrupt sperm production and quality, impair egg development, and increase the risk of infertility. In addition, environmental factors like pollution, radiation, and high levels of occupational stress can also contribute to fertility issues.
11. Exercise
Exercise can have both positive and negative impacts on fertility. Moderate exercise has been associated with improved fertility in both men and women, as it helps maintain healthy body weight, regulate hormone levels, enhance blood circulation, and reduce stress levels.
However, excessive and intense exercise, particularly in women, can lead to disturbances in the menstrual cycle and ovulation. Female athletes or individuals with low body fat may experience irregular periods or stop getting them altogether.
12. Nutrition
An adequate intake of essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fats) are necessary for hormone production, egg and sperm development, and overall reproductive health. Therefore, consuming a diverse diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help promote fertility by providing the necessary nutrients for reproductive processes.
13. Medical conditions
In women, conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and uterine fibroids can disrupt normal hormonal balance and interfere with ovulation and implantation, leading to infertility or reduced fertility.
In men, varicocele and testicular disorders can affect sperm production and quality. Additionally, hormonal disorders, thyroid dysfunction, autoimmune diseases, and certain genetic conditions can also impact fertility in both sexes.
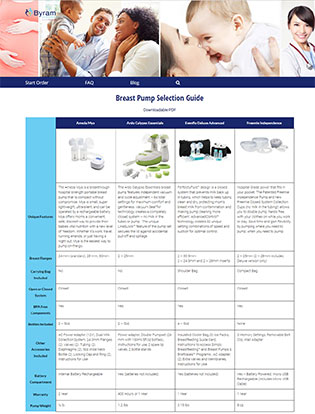
Fertility is a complex issue affected by a variety of factors. If you’re having difficulty conceiving, seeing your doctor to better understand unique contributing factors is important. There are options available for everyone, and if you become a parent, Byram Healthcare is there to help. We offer a wide selection of insurance-covered breast pumps to new and expecting moms, so you can always provide your baby with necessary nutrients. Browse our breast pump comparison chart to learn about the differences today.